Explore the next level of secure, role-based access control with Sage Active's Public API.
A new era of intuitive application development awaits.
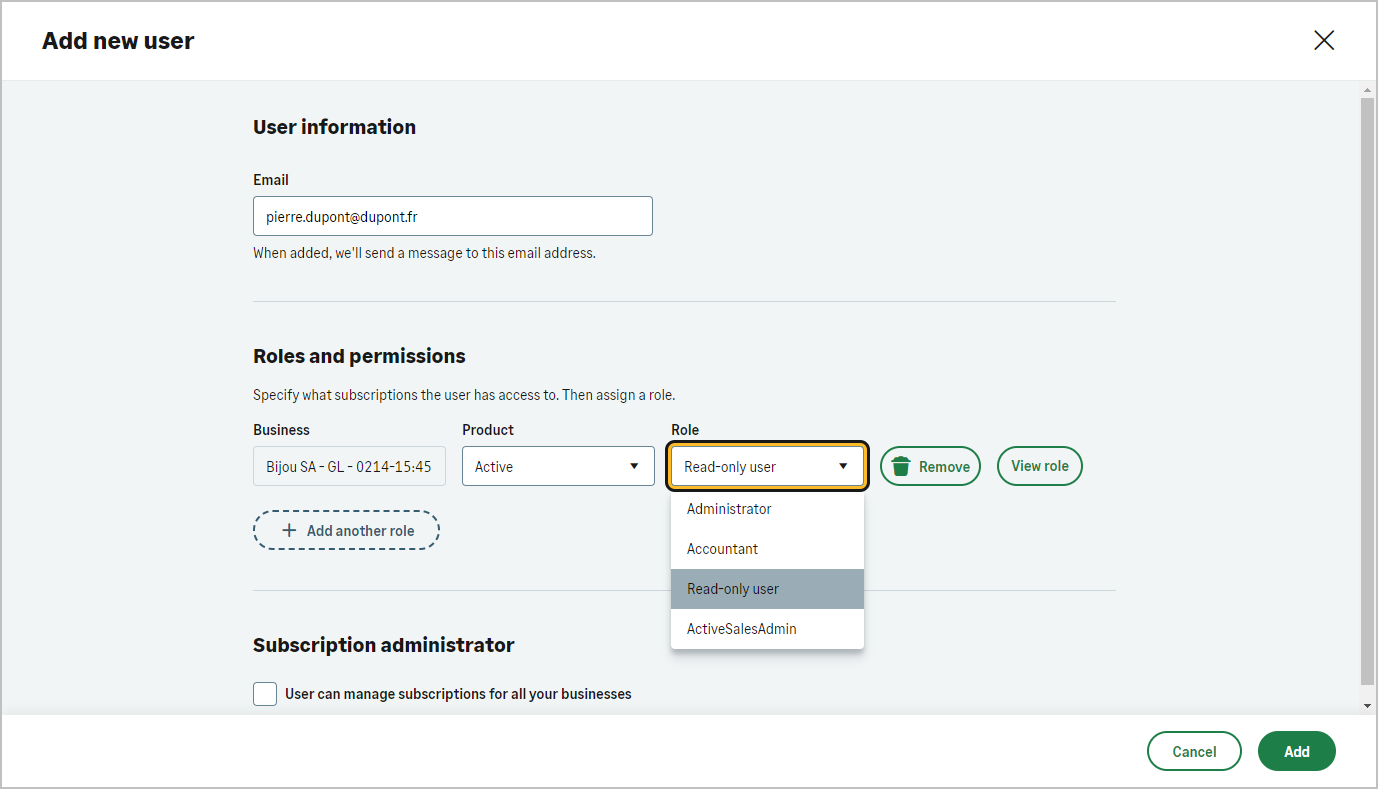
Users management
Quick Links
Accounts Accounting Entries Products Customers Sales quotes Sales invoices Suppliers Purchase invoicesRole Management and Access to Business in Public API
User Management Unleashed: Sage Active Public API's Role-Based Innovation
The public API must apply the same policies defined in these roles to align with the behavior of the Sage Active application.
Furthermore, the Sage Active solution not only considers the user’s role but can also restrict access to certain data based on the Sage Active solution in use.
For the same role, a user may be denied access to certain data depending on whether they are using Sage Active Starter or Sage Active Essentials.
Follow the link for more details on the available Sage Active solutions:
Examples
-
Example 1
If a user has only theAccountantrole, they cannot access features in Sage Active other than those related to accounting.
Similarly, the public API will restrict access for this user to accounting data only. -
Example 2
If a user has only aread-onlyrole, then the public API should not authorize mutations that allow creating, modifying, or deleting data. -
Example 3 If a user has the right to view businesses A and B but not C, then the public API will only allow access to organizations A and B, but not C.
-
Example 4
If the Sage Active solution isStarter, even if a user has theadminrole, they will not be able to access accounting entries.
Role or Feature Error Management
If a query or mutation request is denied due to unauthorized rights, the API will return a message in the form:
Here, for example, if the user has only an Accountant role, and the createProduct object of the public API is called, this error will be returned.
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "global.businessErrors.authorizationPolicy",
"locations": [
{
"line": 1,
"column": 51
}
],
"path": [
"createProduct"
],
"extensions": {
"details": "add-product"
}
}
],
"data": {
"createProduct": null
}
}
- The message will contain:
global.businessErrors.authorizationPolicyif the user’s role does not permit access to the feature.global.businessErrors.authorizationFeatureif the current solution does not authorize the feature.
-
Detailed information can be found in:
"extensions": { "details": "add-product" }
Other Error Handling for Unknown Users in Sage Active
Note that another error may be returned, this time in the case where the user is not authorized at all to use the current business.
This error will then be formatted as follows:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "The current user is not authorized to access this resource.",
"locations": [
{
"line": 2,
"column": 3
}
],
"path": [
"products"
],
"extensions": {
"code": "AUTH_NOT_AUTHORIZED"
}
}
],
"data": {
"products": null
}
}
Predicting User Permissions for Actions
For example, for a user with a read-only role, it’s pointless to offer a Create, Modify, or Delete button.
It’s preferable to disable or hide the button rather than allowing the user to enter data only to receive a message that the action is denied.
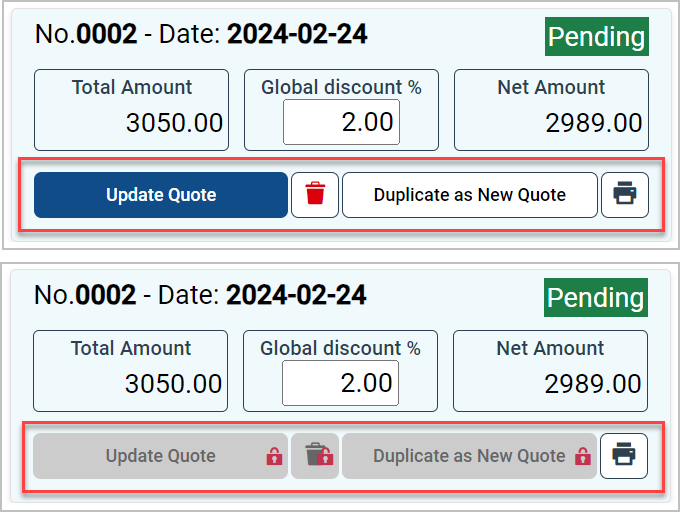
To achieve this, the API resources overview / ⚙️User Access Policy Check action allows passing in parameters like object names (e.g., mutation createCustomer or deleteSalesQuote, query accountingAccounts), and the API will return a true or false for each object name for the current user.
For instance, if the response for the createCustomer parameter is false, it will be possible to act on the application front to disable or remove the Create a Customer button or to inform with a message that this action will not be available.